Abdur Rouf
- Research Assistant
- Department of Computer Engineering
- University of Central Florida
- abdur.rouf [AT] ucf.edu
- +1 (929) 372 5182

My current research spans reinforcement learning–driven optimization and large-scale distributed experimentation for next-generation networked systems. I focus on intelligent flow management in Software-Defined Networking (SDN), efficient state encoding for Deep Q-Network (DQN)–based decision systems, and speculative transport protocols capable of predicting future traffic patterns.
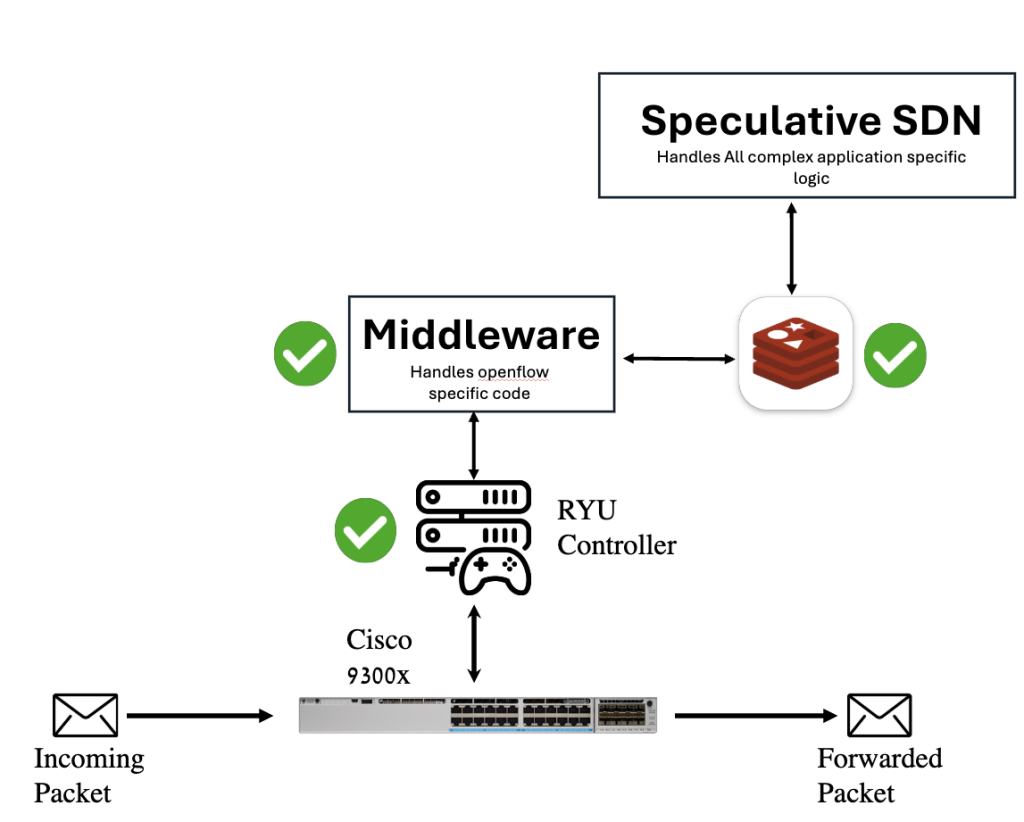
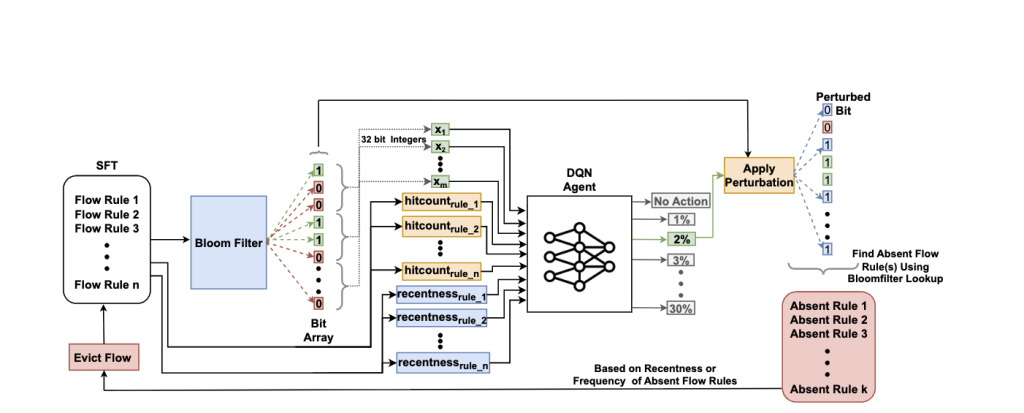

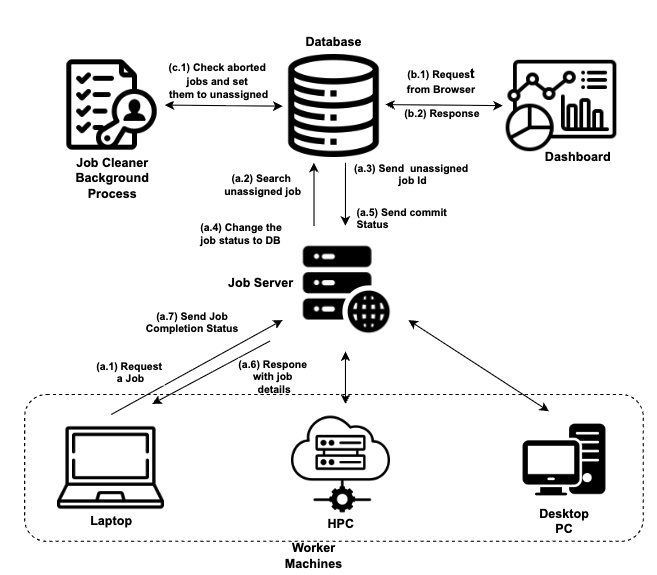
This ongoing project explores how reinforcement learning can be used to design speculative transport protocols. The goal is to predict future bytes or packet sequences before they arrive, enabling ultra-fast, low-latency communication. By modeling traffic behavior and learning predictive patterns, this system aims to augment or replace traditional TCP-style reactive transport mechanisms.